Welcome to BKPOWER!

How to Calculate Watts: A Practical Guide
Introduction
Understanding how to calculate watts is essential for various electrical applications, from selecting the right UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) system to ensuring your devices receive the proper power. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to protect your computer setup or a business owner aiming to safeguard critical equipment, knowing how to figure out watts can help you make informed decisions. In this article, we will explore the concept of watts, the formula for calculating watts, and provide practical examples to help you apply this knowledge in real – world scenarios. As a leading provider of power solutions, BKPOWER is committed to empowering you with the information needed to ensure reliable power protection.

What Are Watts?
Watts (W) are the basic unit of power in electrical systems. They represent the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or produced. In simpler terms, watts indicate how much power a device uses or generates over time.
The Formula for Calculating Watts
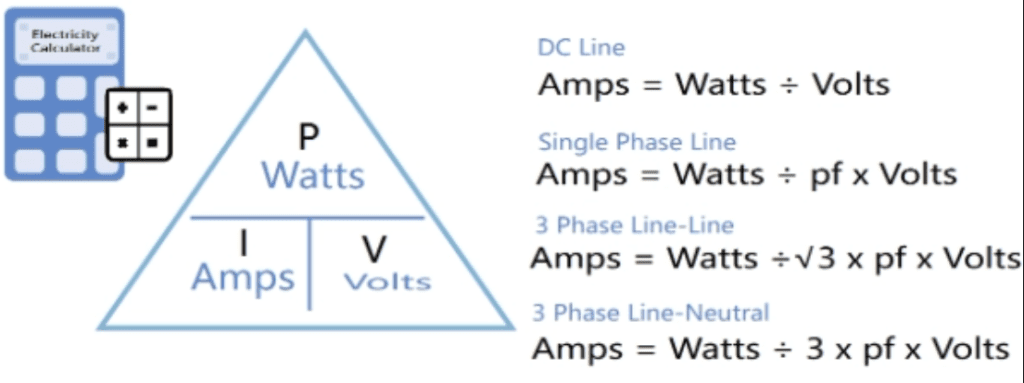
The fundamental formula for calculating watts is:
Watts (P) = Volts (V) × Amps (I)
Where:
- P represents power in watts
- V represents voltage in volts
- I represents current in amps
This formula, also known as Watt’s Law, shows the relationship between power, voltage, and current.
Steps to Calculate Watts
- Determine Voltage :Check the voltage rating of your device or power source. Common household voltage is 120V or 240V, while industrial systems may use higher voltages.
- Measure Current :Use a multimeter to measure the current (in amps) flowing through the circuit, or refer to the device specifications for the current rating.
- Apply the Formula :Multiply the voltage by the current to get the power in watts.
Practical Examples
- Example 1:Calculating the power consumption of a light bulb rated at 120V and drawing 0.5 amps.
- Watts = 120V × 0.5A = 60W
- Example 2:Determining the power output of a solar panel producing 24V and 3 amps.
- Watts = 24V × 3A = 72W
Calculating Watts for UPS Systems
When it comes to UPS systems, calculating watts is crucial for proper sizing and ensuring adequate power protection.
- Step 1:Identify the power requirements of your devices by checking their wattage ratings. Add up the wattage of all devices to be connected to the UPS.
- Step 2:Consider the power factor if using AC power. The formula becomes Watts = Volts × Amps × Power Factor. Typical power factors range from 0.7 to 1.0 for most electronic devices.
- Step 3:Select a UPS with a power rating higher than your total wattage to account for power surges and future expansion.
Example Calculation for UPS
Suppose you have the following devices:
- Computer: 200W
- Monitor: 50W
- Router: 10W
Total wattage = 200W + 50W + 10W = 260W
Choose a UPS with a minimum power rating of 300W to 400W to ensure reliable protection.
Factors Affecting Wattage Calculations
- Power Factor:As mentioned earlier, the power factor is essential in AC systems. It represents the ratio of real power (watts) to apparent power (volt – amps). A low power factor means more reactive power is present, affecting the overall efficiency.
- Efficiency Losses:No system is 100% efficient. Account for energy losses in power converters and transformers, especially when calculating watts for UPS systems.
- Voltage Fluctuations:Voltage sags or surges can impact current flow, leading to variations in power consumption. Consider using a UPS with automatic voltage regulation to stabilize power.
Tips for Accurate Wattage Measurements
- Use Power Meters:Devices like power meters can directly measure the wattage of appliances, providing accurate data without complex calculations.
- Consult Manufacturer Specifications:Reliable information about voltage and current requirements is usually available in the device’s user manual or on its specification plate.
- Consider Surge Wattage:Some devices, like motors, require a surge of power to start. Ensure your UPS can handle the initial surge wattage, which may be several times higher than the running wattage.
Applications in Power Protection
- UPS Sizing:Accurately calculating watts ensures your UPS can handle your equipment’s power demands. An undersized UPS may overload and fail, while an oversized one may be cost – prohibitive.
- Energy Cost Estimation:Knowing the wattage helps estimate energy consumption and costs over time, aiding in budgeting for electricity expenses.
- Equipment Compatibility:Ensures that your devices and power sources are compatible, preventing damage from over – or under – powering.
BKPOWER’s Expertise in Power Solutions
At BKPOWER, we specialize in providing reliable power solutions tailored to various needs. Our UPS systems are designed with advanced technology to deliver precise power protection. We understand the importance of accurate wattage calculations in ensuring uninterrupted power supply. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in selecting the right UPS system and calculating the necessary power requirements for your specific setup.
Conclusion
Calculating watts is a fundamental skill in electrical systems that helps in selecting the appropriate UPS and ensuring efficient power usage. By following the steps outlined in this article and considering the factors that affect wattage, you can make informed decisions for your power protection needs. BKPOWER is dedicated to offering high – quality UPS systems and supporting you in maintaining reliable power for your devices.
Visit BKPOWER’s website at www.bkpower.cn to explore our range of UPS systems and discover how we can help you calculate and meet your power protection requirements.
References
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)Official website: www.iec.ch
- Underwriters Laboratories (UL)Official website: www.ul.com
- European Committee for Standardization (CEN)Official website: www.cen.eu
- Standardization Administration of China (SAC)Official website: www.sac.gov.cn
- Zhongguancun Energy Storage Industry Technology Alliance (CNESA)Official website: www.cnESA.org
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO)Official website: www.iso.org
.png)
.png)
