Welcome to BKPOWER!

Exploring 2 Phase Electricity and Its UPS Solutions
In the diverse landscape of electrical power systems, while single – phase and three – phase electricity often take the spotlight, 2 – phase electricity, though less common, holds its own significance and unique applications. Understanding 2 – phase electricity is crucial for specific industrial, commercial, and even some specialized residential setups. In this in – depth article, we’ll delve into the details of 2 – phase electricity, including its working principles, characteristics, applications, and how it compares with single – phase and three – phase systems. Moreover, we’ll explore how BKPOWER, a leading provider of Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) solutions, offers tailored UPS products for 2 – phase electricity environments, ensuring reliable power protection and seamless operation.

Ⅰ. Introduction to 2 – Phase Electricity
1. Definition and Concept
2 – phase electricity, also known as two – wire – two – phase or split – phase in some contexts, is an alternating – current (AC) power system that consists of two sinusoidal voltages or currents that are out of phase with each other by 90 degrees. In a traditional 2 – phase system, there are typically two live wires and sometimes a neutral wire depending on the configuration. This phase difference of 90 degrees creates a more balanced power delivery compared to single – phase systems and has certain advantages in specific applications.
Mathematically, if we represent the voltage of one phase as

the voltage of the other phase can be expressed as
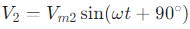
where

are the maximum voltages of the two phases,ω is the angular frequency, and t is time.
2. Historical Background
2 – phase electricity had its heyday in the early days of the electrical industry. It was widely used in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, especially for powering electric motors and lighting systems in some regions. However, as the electrical infrastructure evolved, three – phase systems gradually became more popular due to their higher power – transmission efficiency and better suitability for large – scale industrial applications. Despite this, 2 – phase electricity still persists in certain niche areas where its unique characteristics make it a preferred choice.
Ⅱ. Working Principles of 2 – Phase Electricity
1. Generation
2 – phase electricity can be generated in power plants using specialized generators. Inside the generator, two sets of coils are arranged at a 90 – degree angle to each other. As the generator’s rotor spins, it creates a magnetic field that induces alternating currents in these two sets of coils. Due to the 90 – degree angular arrangement of the coils, the induced currents in each coil have a 90 – degree phase difference, resulting in the characteristic 2 – phase output.
2. Transmission and Distribution
Once generated, 2 – phase electricity is transmitted over power lines to the end – users. Similar to other electrical systems, it may pass through transformers at substations to adjust the voltage to an appropriate level for distribution. In the distribution network, the two – phase power is delivered to the consumer premises, where it can be used to power various electrical devices that are designed to operate on 2 – phase electricity.
Ⅲ. Characteristics of 2 – Phase Electricity
1. Power Delivery
Compared to single – phase electricity, 2 – phase systems can deliver a more balanced and continuous power supply. The 90 – degree phase difference between the two phases helps to smooth out the power fluctuations, which is beneficial for powering certain types of motors and electrical equipment. This balanced power delivery can result in reduced vibration and noise in motors, leading to longer equipment lifespan and more efficient operation.
2. Voltage and Current
In a 2 – phase system, the voltage between the two live wires is typically higher than the voltage in a single – phase system. The exact voltage values can vary depending on the region and the specific application. For example, in some older systems, the voltage between the two phases might be around 240 volts, while the voltage from each phase to the neutral (if present) could be 120 volts. The current in a 2 – phase system also has its own characteristics, with the two – phase currents interacting in a way that affects the overall power consumption and performance of the connected devices.
Ⅳ. Applications of 2 – Phase Electricity
1. Industrial Applications
In certain industrial settings, 2 – phase electricity is still used, especially for powering specific types of motors. Some older manufacturing plants or facilities with legacy equipment may rely on 2 – phase motors for tasks such as conveyor belt operations, small – scale machining, and certain types of pumps. The balanced power delivery of 2 – phase systems can be advantageous for these applications, ensuring smooth and reliable operation of the machinery.
2. Commercial and Residential Applications
In some commercial buildings, particularly those with specialized electrical requirements, 2 – phase electricity might be utilized for powering equipment like certain types of air – conditioning units, lighting systems with specific design considerations, or small – scale electrical distribution systems. In rare cases, some older residential areas or custom – built homes with unique electrical setups may also incorporate 2 – phase electricity for specific appliances or systems.
Ⅴ. Comparison with Single – Phase and Three – Phase Electricity
1. 2 – Phase vs Single – Phase
- Power Capacity: 2 – phase systems generally have a higher power – delivering capacity than single – phase systems. The balanced power output of 2 – phase allows for more efficient operation of certain electrical devices, especially motors, compared to the unidirectional power flow in single – phase systems.
- Efficiency: In terms of power transmission and utilization for specific applications, 2 – phase electricity can offer better efficiency. The reduced power fluctuations and more balanced current flow result in lower energy losses and improved performance of connected equipment. However, single – phase systems are simpler and more commonly used in low – power residential and small – scale commercial applications due to their ease of installation and lower cost.
2. 2 – Phase vs Three – Phase
- Power Capacity: Three – phase systems have a significantly higher power – delivering capacity compared to 2 – phase systems. The three – phase configuration with its 120 – degree phase difference allows for the transmission of much larger amounts of power, making it the preferred choice for large – scale industrial and commercial applications.
- Complexity and Cost: 2 – phase systems are less complex than three – phase systems. They require fewer wires and less complex electrical equipment in some cases, which can result in lower installation and maintenance costs. However, three – phase systems offer better overall efficiency and reliability for high – power applications, despite the higher initial investment.
Ⅵ. UPS Requirements for 2 – Phase Electricity Systems
1. Special Considerations
When it comes to providing backup power for 2 – phase electricity systems, UPS units need to be specifically designed to handle the unique characteristics of 2 – phase power. This includes the ability to accurately detect and respond to voltage and current changes in the two – phase system, as well as the capacity to provide stable backup power with the correct phase relationship. A UPS for a 2 – phase system must also be able to handle the specific power requirements of the connected devices, ensuring seamless operation during power outages.
2. Key Features of 2 – Phase UPS
- Phase – Sensitive Design: A 2 – phase UPS should have a phase – sensitive design that can monitor and maintain the 90 – degree phase difference between the two phases. This ensures that the backup power provided is consistent with the requirements of the connected 2 – phase equipment.
- Voltage Regulation: Similar to other UPS systems, a 2 – phase UPS needs to have effective voltage regulation capabilities. It should be able to stabilize the incoming 2 – phase voltage during normal operation and provide a stable output voltage during backup mode to protect the connected devices from voltage fluctuations.
- Battery Capacity and Management: Adequate battery capacity is crucial for a 2 – phase UPS to provide sufficient backup time. Additionally, an intelligent battery management system is necessary to optimize battery charging and discharging, extend the battery lifespan, and ensure reliable performance during power outages.
Ⅶ. BKPOWER’s 2 – Phase UPS Solutions
1. Product Range
BKPOWER offers a comprehensive range of UPS products specifically designed for 2 – phase electricity systems. Our 2 – phase UPS units are available in various capacities, ranging from small – scale models suitable for protecting essential equipment in commercial buildings or small industrial setups to high – capacity units capable of supporting large – scale 2 – phase electrical systems in industrial facilities.
2. Advanced Technologies
- Phase – Sensitive Inverters: Our 2 – phase UPS systems are equipped with advanced phase – sensitive inverters that can precisely control the phase relationship between the two output phases. This ensures that the backup power provided is a perfect match for the connected 2 – phase devices, preventing any potential damage due to incorrect phase alignment.
- Intelligent Voltage Regulation: BKPOWER’s 2 – phase UPS products feature intelligent voltage regulation technology. They can automatically detect voltage fluctuations in the 2 – phase input and adjust the output voltage in real – time, providing a stable and clean power supply to the connected equipment. This not only protects the devices from voltage – related issues but also improves the overall efficiency of the electrical system.
- High – Quality Batteries and Battery Management: We use high – quality batteries in our 2 – phase UPS units, sourced from leading manufacturers. These batteries offer high energy density, long lifespan, and fast charging capabilities. Coupled with our intelligent battery management system monitors, which battery status, optimizes charging, and provides early warnings for potential battery issues, our 2 – phase UPS solutions ensure reliable and long – lasting backup power.
3. Customization and Support
Understanding that different 2 – phase electricity systems have unique requirements, BKPOWER offers customization options for our 2 – phase UPS products. Our team of experts can work closely with customers to assess their specific power needs, equipment configurations, and backup time requirements, and then tailor a UPS solution that meets their exact specifications. Additionally, we provide comprehensive after – sales support, including installation guidance, maintenance services, and technical assistance, ensuring that our customers have a worry – free experience with our 2 – phase UPS products.
Ⅷ. Conclusion
2 – phase electricity, although not as prevalent as single – phase and three – phase systems, has its own distinct place in the electrical power industry. Its unique characteristics, such as balanced power delivery and specific voltage – current relationships, make it suitable for certain industrial, commercial, and residential applications. When it comes to ensuring reliable backup power for 2 – phase electricity systems, BKPOWER’s range of specialized 2 – phase UPS solutions stands out. With advanced technologies, high – quality components, and customizable options, our 2 – phase UPS products provide the perfect combination of reliability, efficiency, and performance. Whether you’re operating an industrial facility with 2 – phase equipment, managing a commercial building with specific electrical requirements, or dealing with a unique residential electrical setup, BKPOWER has the right 2 – phase UPS solution for you. Contact us today to explore our product offerings and experience the difference in power protection for 2 – phase electricity systems.
References
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)Official website: www.iso.org
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)Official website: www.iec.ch
Underwriters Laboratories (UL)Official website: www.ul.com
European Committee for Standardization (CEN)Official website: www.cen.eu
Standardization Administration of China (SAC)Official website: www.sac.gov.cn
Zhongguancun Energy Storage Industry Technology Alliance (CNESA)Official website: www.cnESA.org
.png)
.png)

